Intro: The way to exploit the V8 typer bug
Patch
在之前的 V8 exploit 过程中,利用 typer 漏洞的案例有很多,而且几乎都用到了 Simplified lowering 来做边界消除:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17void VisitCheckBounds(Node* node, SimplifiedLowering* lowering) {
···
if (lower()) {
if (lowering->poisoning_level_ ==
PoisoningMitigationLevel::kDontPoison &&
(index_type.IsNone() || length_type.IsNone() ||
(index_type.Min() >= 0.0 &&
index_type.Max() < length_type.Min()))) {
// The bounds check is redundant if we already know that
// the index is within the bounds of [0.0, length[.
DeferReplacement(node, node->InputAt(0));
} else {
NodeProperties::ChangeOp(
node, simplified()->CheckedUint32Bounds(p.feedback()));
}
}
···
然而,在 commit 7bb6dc0e06fa158df508bc8997f0fce4e33512a5 中加入了如下 patch(节选部分):
【+】首先在 Simplified lowering :
可见,改变了原先直接消除节点的方式,转而将所有 CheckBound 节点全部 lower 成 CheckedUint32Bounds,根据不同的条件给 CheckedUint32Bounds 节点赋予不同的 mode。
【+】其次是 Effect ControlLinearizer:
虽然根据不同的 mode 采取不同的 lowing,但是均会 lowing 到 Uint32LessThan。不同的是 kDeoptOnOutOfBounds 会判断是否溢出从而判断是否 deopt; kAbortOnOutOfBounds mode 则是对于 if_abort (溢出)状态直接给予 Unreachable 作为后继,Unreachable 节点后续会在 InstructionSelector 被 breakpoint 取代:1
2
3
4void InstructionSelector::VisitUnreachable(Node* node) {
OperandGenerator g(this);
Emit(kArchDebugBreak, g.NoOutput());
}
但这里值得注意的是,Uint32LessThan 会在 TFLateOptimization 中被 lower 成 Int32Constant 。由于 Turbofan 在 LateOptimization 中加入了如下众多的 reducer:1
2
3
4
5
6AddReducer(data, &graph_reducer, &branch_condition_elimination);
AddReducer(data, &graph_reducer, &dead_code_elimination);
AddReducer(data, &graph_reducer, &machine_reducer);
AddReducer(data, &graph_reducer, &common_reducer);
AddReducer(data, &graph_reducer, &select_lowering);
AddReducer(data, &graph_reducer, &value_numbering);
其中包含 dead_code_elimination 以及 machine_reducer。在这些 reducer 运作的过程中, Uint32LessThan 会被 MachineOperatorReducer(machine_reducer) 替换为 Int32Constant :1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25//machine-operator-reducer.cc:283
case IrOpcode::kUint32LessThan: {
Uint32BinopMatcher m(node);
if (m.left().Is(kMaxUInt32)) return ReplaceBool(false); // M < x => false
if (m.right().Is(0)) return ReplaceBool(false); // x < 0 => false
if (m.IsFoldable()) { // K < K => K
return ReplaceBool(m.left().Value() < m.right().Value());
}
if (m.LeftEqualsRight()) return ReplaceBool(false); // x < x => false
if (m.left().IsWord32Sar() && m.right().HasValue()) {
Int32BinopMatcher mleft(m.left().node());
if (mleft.right().HasValue()) {
// (x >> K) < C => x < (C << K)
// when C < (M >> K)
const uint32_t c = m.right().Value();
const uint32_t k = mleft.right().Value() & 0x1F;
if (c < static_cast<uint32_t>(kMaxInt >> k)) {
node->ReplaceInput(0, mleft.left().node());
node->ReplaceInput(1, Uint32Constant(c << k));
return Changed(node);
}
// TODO(turbofan): else the comparison is always true.
}
}
如果满足 m.IsFoldable() 即 left().HasValue() && right().HasValue(),则经过1
2
3if (m.IsFoldable()) { // K < K => K
return ReplaceBool(m.left().Value() < m.right().Value());
}
Uint32LessThan 最终被替换为 Int32Constant[0/1]。
同时,如果 Uint32LessThan 后边紧跟 Branch 节点,则该 Branch node 以及后续一定不会触发的分支会被 CommonOperatorReducer 优化为 Dead;一定会触发的分支则会被合并到上一级 control:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16Decision const decision = DecideCondition(js_heap_broker(), cond);
if (decision == Decision::kUnknown) return NoChange();
Node* const control = node->InputAt(1);
for (Node* const use : node->uses()) {
switch (use->opcode()) {
case IrOpcode::kIfTrue:
Replace(use, (decision == Decision::kTrue) ? control : dead());
break;
case IrOpcode::kIfFalse:
Replace(use, (decision == Decision::kFalse) ? control : dead());
break;
default:
UNREACHABLE();
}
}
return Replace(dead());
于是接着在 DeadCodeElimination 中 Unreachable 节点将会被替换为 Dead:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14Reduction DeadCodeElimination::ReduceUnreachableOrIfException(Node* node) {
DCHECK(node->opcode() == IrOpcode::kUnreachable ||
node->opcode() == IrOpcode::kIfException);
Reduction reduction = PropagateDeadControl(node);
if (reduction.Changed()) return reduction;
Node* effect = NodeProperties::GetEffectInput(node, 0);
if (effect->opcode() == IrOpcode::kDead) {
return Replace(effect);
}
if (effect->opcode() == IrOpcode::kUnreachable) {
return Replace(effect);
}
return NoChange();
}
自然也就避免了变为breakpoint;同时将 Branch 原先选择分支的行为优化为单一控制流。
等等,发生了什么?
我们中通过上述的分析最终消除了 Branch 的另一分支,这不是恰好和 Simplified lowering 的最终效果类似吗?
仔细思考一下,也就是说,如果我们想通过 Typer 的漏洞来实现 exploit,需要将编译器行为固定为:
Simplified lowering:CheckBound节点转化为CheckedUint32BoundsSimplified lowering:CheckedUint32Bounds mode为kAbortOnOutOfBoundsEffect ControlLinearizer:CheckedUint32Boundslowing成Uint32LessThan;Uint32LessThan包含Unreachable作为if_abort状态的后继。LateOptimization:Uint32LessThan转化为Int32Constant[1], 使得后续的DeadCodeElimination reducer将Branch节点优化为Dead的同时削减一条分支,在这里我们要控制削减的那条为Unreachable分支。
Deeemo
1 | var opt_me = () => { |
- Typer
- SimplifiedLowing

CheckBound节点转化为CheckUint32Bounds - EffectLinearization
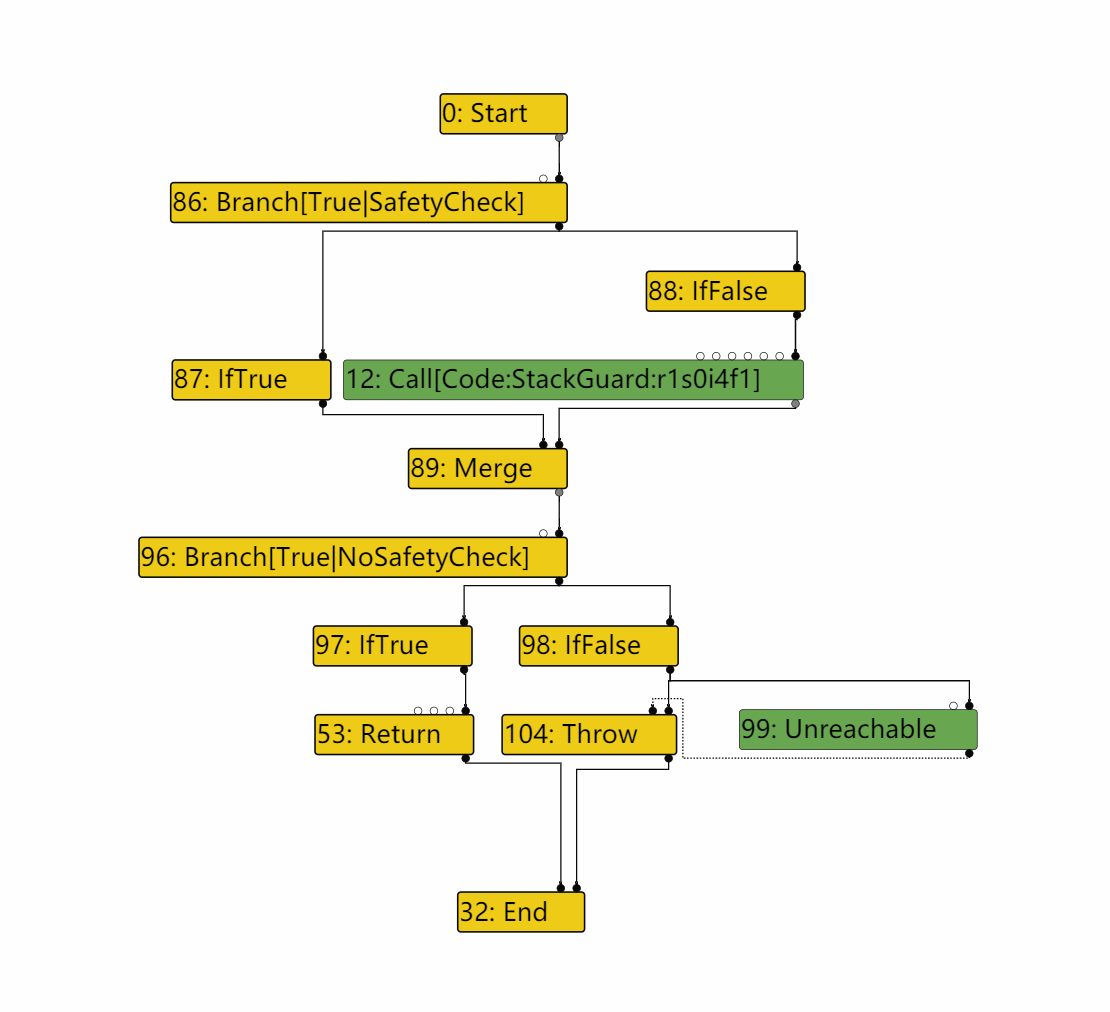
CheckUint32Bounds转化为Uint32LessThan,同时可以看到Branch节点的一个分支为Unreachable。
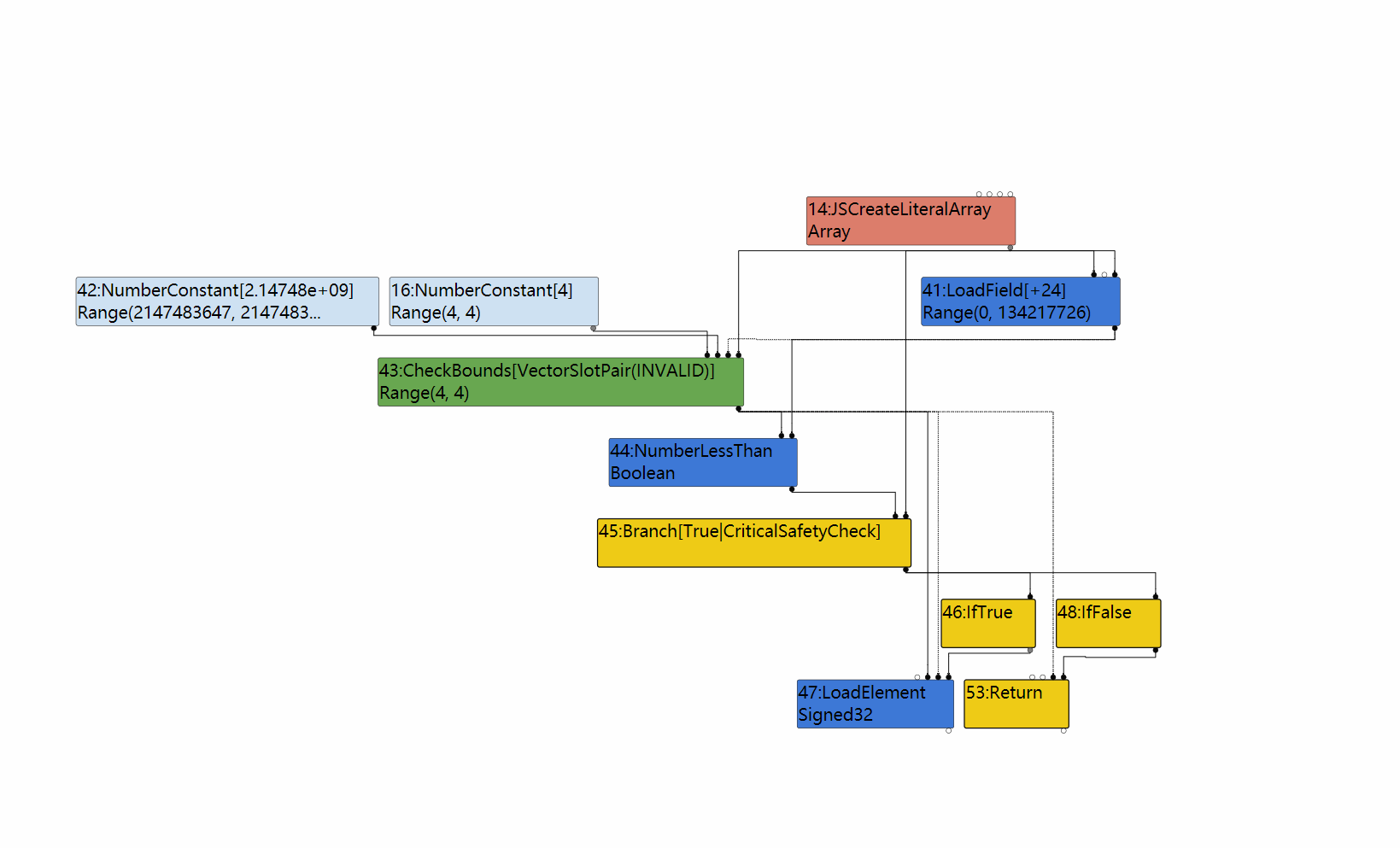
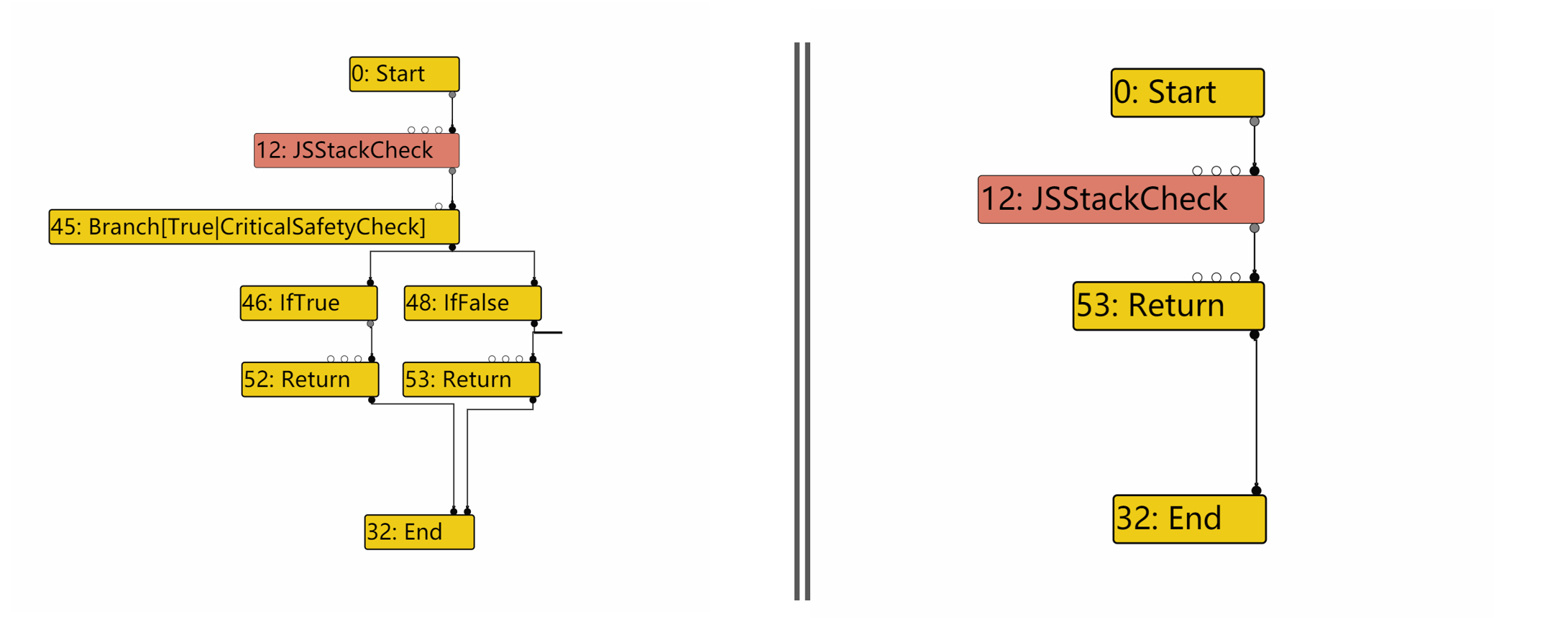
4.LateOptimize 可以看到
可以看到 89节点在EffectLinearization phase中的后继只留下了IfTrue之后的53:Return,IfFalse分支被全部剪掉了。
四个过程的行为和第一部分的介绍非常一致。但是奇怪的是,47 节点 LoadElement消失了,虽然该 node 的消失并非我们探寻 typer bug 利用的过程中的重点,但是有助于我们理解为何针对 Simplified lowering 的 patch 会增强安全性。
消失的 LoadElement 节点
观察 Turbolizer:
LoopPeeling 之后:
LoadElimination 之后: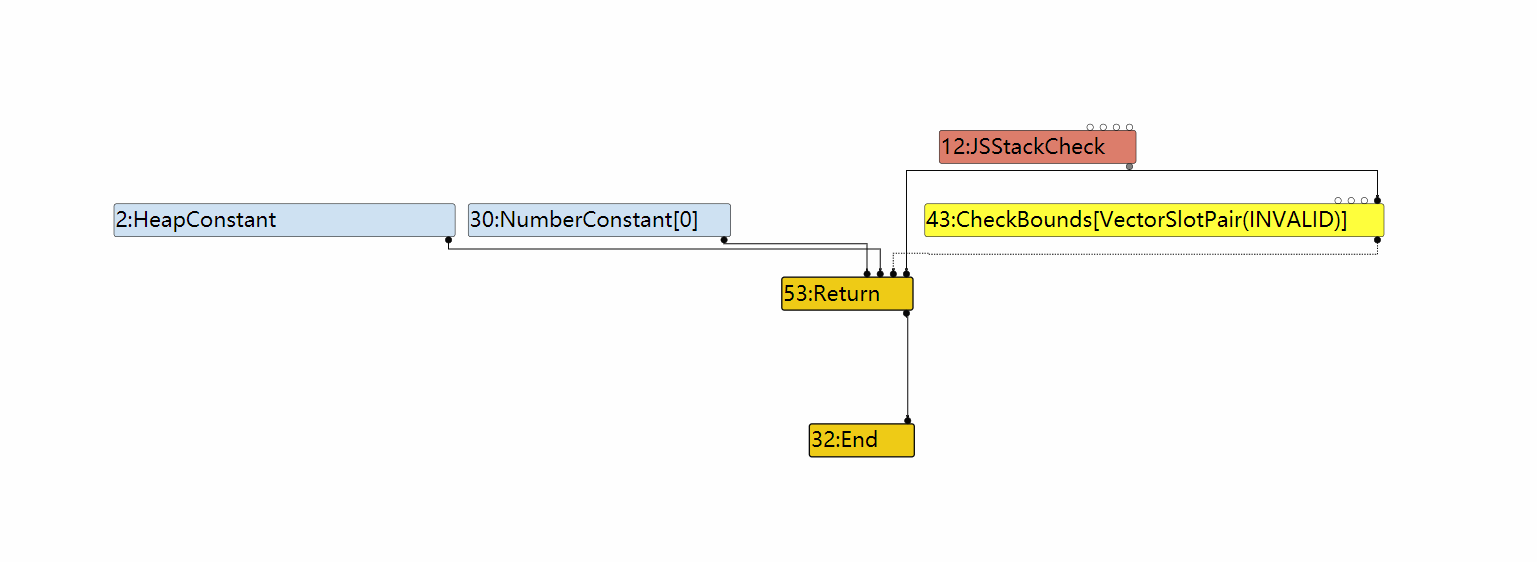
可见,47:LoadElement 节点在 LoadElimination 中被优化掉。而该节点正是加载元素值的节点。注意到,原 POC 中针对 arr的访问其实是越界的,因此该 load 节点的消失从逻辑上无可非议。然而分析并不能到此为止,我们需要知道 V8 以什么方法去除该节点以及绕过技巧。
V8 如何处理
首先关注 LoadEliminate 的控制流变化:
可以看到,经过了 LoadEliminate 之后的控制流恰好剪掉了 True 分支,而 True 分支的 return 节点是 loadelement的 use节点。由于该分支被剪掉,直接导致了后续的控制流将没有任何机会接触到 load 节点。影响之一就是在 EffectLinearization 中,Contro flow 是如下形式:
因此错过了 load value 的机会。
控制流分析完毕,下面我打算关注具体的代码实现:
首先通过观察 --trace-turbo-reduction:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8- In-place update of 43: CheckBounds[VectorSlotPair(INVALID)](16, 42, 17, 12) by reducer RedundancyElimination
- In-place update of 43: CheckBounds[VectorSlotPair(INVALID)](16, 42, 17, 12) by reducer LoadElimination
- In-place update of 44: NumberLessThan(43, 16) by reducer TypeNarrowingReducer
- Replacement of 44: NumberLessThan(43, 16) with 55: HeapConstant[0x2d168800046d <false>] by reducer ConstantFoldingReducer
- In-place update of 45: Branch[True|CriticalSafetyCheck](55, 12) by reducer BranchElimination
- Replacement of 45: Branch[True|CriticalSafetyCheck](55, 12) with 70: Dead by reducer CommonOperatorReducer
- Replacement of 47: LoadElement[tagged base, 8, Signed31, kRepCompressedSigned|kTypeInt32, FullWriteBarrier](59, 43, 43, 70) with 70: Dead by reducer DeadCodeElimination
- Replacement of 52: Return(30, 70, 70, 70) with 70: Dead by reducer DeadCodeElimination
发现:
44: NumberLessThan(43, 16)节点的的输入更新为 43 和 16 其中,16节点为NumberConstant[4]44: NumberLessThan(43, 16)节点被ConstantFoldingReducer优化为false45: Branch(55, 12)节点被 CommonOperatorReducer优化为dead,47: LoadElement节点以及52: Return节点被DeadCodeElimination优化为dead。至此完成了True分支的消除
可知,关键在于 44: NumberLessThan(43, 16) 节点的 false 替换,直接导致了后面的剪枝。
鉴于以上的初步分析,下面具体看一下源码
源码分析
首先是导致 44: NumberLessThan(43, 16) 变为 false 的 ConstantFoldingReducer:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44Reduction ConstantFoldingReducer::Reduce(Node* node) {
DisallowHeapAccess no_heap_access;
// Check if the output type is a singleton. In that case we already know the
// result value and can simply replace the node if it's eliminable.
if (!NodeProperties::IsConstant(node) && NodeProperties::IsTyped(node) &&
node->op()->HasProperty(Operator::kEliminatable)) {
// TODO(v8:5303): We must not eliminate FinishRegion here. This special
// case can be removed once we have separate operators for value and
// effect regions.
if (node->opcode() == IrOpcode::kFinishRegion) return NoChange();
// We can only constant-fold nodes here, that are known to not cause any
// side-effect, may it be a JavaScript observable side-effect or a possible
// eager deoptimization exit (i.e. {node} has an operator that doesn't have
// the Operator::kNoDeopt property).
Type upper = NodeProperties::GetType(node);
if (!upper.IsNone()) {
Node* replacement = nullptr;
if (upper.IsHeapConstant()) {
replacement = jsgraph()->Constant(upper.AsHeapConstant()->Ref());
} else if (upper.Is(Type::MinusZero())) {
Factory* factory = jsgraph()->isolate()->factory();
ObjectRef minus_zero(broker(), factory->minus_zero_value());
replacement = jsgraph()->Constant(minus_zero);
} else if (upper.Is(Type::NaN())) {
replacement = jsgraph()->NaNConstant();
} else if (upper.Is(Type::Null())) {
replacement = jsgraph()->NullConstant();
} else if (upper.Is(Type::PlainNumber()) && upper.Min() == upper.Max()) {
replacement = jsgraph()->Constant(upper.Min());
} else if (upper.Is(Type::Undefined())) {
replacement = jsgraph()->UndefinedConstant();
}
if (replacement) {
// Make sure the node has a type.
if (!NodeProperties::IsTyped(replacement)) {
NodeProperties::SetType(replacement, upper);
}
ReplaceWithValue(node, replacement);
return Changed(replacement);
}
}
}
return NoChange();
}
看到,只根据 node 的 type 进行替换。因此推断,前面的 typer 更新了 NumberLessThan(43, 16) 节点的 type,回溯上文,注意到一个敏感 In-place update:1
- In-place update of 44: NumberLessThan(43, 16) by reducer TypeNarrowingReducer
OK,研究一下 TypeNarrowingReducer1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32Reduction TypeNarrowingReducer::Reduce(Node* node) {
DisallowHeapAccess no_heap_access;
Type new_type = Type::Any();
switch (node->opcode()) {
case IrOpcode::kNumberLessThan: {
// TODO(turbofan) Reuse the logic from typer.cc (by integrating relational
// comparisons with the operation typer).
Type left_type = NodeProperties::GetType(node->InputAt(0));
Type right_type = NodeProperties::GetType(node->InputAt(1));
if (left_type.Is(Type::PlainNumber()) &&
right_type.Is(Type::PlainNumber())) {
if (left_type.Max() < right_type.Min()) {
new_type = op_typer_.singleton_true();
} else if (left_type.Min() >= right_type.Max()) {
new_type = op_typer_.singleton_false();
}
}
break;
}
...
Type original_type = NodeProperties::GetType(node);
Type restricted = Type::Intersect(new_type, original_type, zone());
if (!original_type.Is(restricted)) {
NodeProperties::SetType(node, restricted);
return Changed(node);
}
...
}
很明显,TypeNarrowingReducer 针对 NumberLessThan 有 Type 的更新,对于 left_type.Min() >= right_type.Max() 的情况,新的 singleton_false_ 会取代原本的 Type,进而被 ConstantFoldingReducer 优化为 false 节点,因此之后造成了剪枝。
如何绕过
根据上文的分析,绕过剪枝的关键在于避免 NumberLessThan 节点在 TypeNarrowingReducer 处的优化,因此绕过的关键在于绕过
left_type.Min() >= right_type.Max()
Bypass(1)
在 LoadElimination phase 中的 TypeNarrowingReducer 尚未作用时,44: NumberLessThan(43, 16) 节点的输入分别为 43: CheckBounds 和 16: NumberConstant[4]。如需绕过条件 left_type.Min() >= right_type.Max() 则需要保证
左节点 43: CheckBounds 的 range 最小值小于 4。
追踪 IR 图,可以发现 43: CheckBounds 节点的 Range 在 Typer Phase 中就已经确定:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14Type Typer::Visitor::TypeCheckBounds(Node* node) {
Type index = Operand(node, 0);
Type length = Operand(node, 1);
DCHECK(length.Is(Type::Unsigned31()));
if (index.Maybe(Type::MinusZero())) {
index = Type::Union(index, typer_->cache_.kSingletonZero, zone());
}
index = Type::Intersect(index, Type::Integral32(), zone());
if (index.IsNone() || length.IsNone()) return Type::None();
double min = std::max(index.Min(), 0.0);
double max = std::min(index.Max(), length.Max() - 1);
if (max < min) return Type::None();
return Type::Range(min, max, zone());
}
index 为一个单一常数,因此经过 Typer,CheckBounds 的 range 变成了 Range(4,4)。但我们想让左值小于 4。因此考虑构造一个如下的 POC(参考长亭实验室文章)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8var opt_me = () => {
let arr = [1,2,3,4];
let index = 4;
index = index & 0xfff
return arr[index];
};
for (var i = 0; i < 0x10000; ++i)
opt_me();
可见,新增了 SpeculativeNumberBitwiseAnd 节点。该节点的 Typer 如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30Type OperationTyper::NumberBitwiseAnd(Type lhs, Type rhs) {
DCHECK(lhs.Is(Type::Number()));
DCHECK(rhs.Is(Type::Number()));
lhs = NumberToInt32(lhs);
rhs = NumberToInt32(rhs);
if (lhs.IsNone() || rhs.IsNone()) return Type::None();
double lmin = lhs.Min();
double rmin = rhs.Min();
double lmax = lhs.Max();
double rmax = rhs.Max();
double min = kMinInt;
// And-ing any two values results in a value no larger than their maximum.
// Even no larger than their minimum if both values are non-negative.
double max =
lmin >= 0 && rmin >= 0 ? std::min(lmax, rmax) : std::max(lmax, rmax);
// And-ing with a non-negative value x causes the result to be between
// zero and x.
if (lmin >= 0) {
min = 0;
max = std::min(max, lmax);
}
if (rmin >= 0) {
min = 0;
max = std::min(max, rmax);
}
return Type::Range(min, max, zone());
}
因此经过该 Typer, SpeculativeNumberBitwiseAnd 节点的 Range 最终被确定为 Range(0,4),顺利地传递到 CheckBound 节点,完成绕过。
Bypass(2)
第二种方法在于利用 escape analysis。
POC:1
2
3
4
5
6
7var opt_me = () => {
let arr = [1,2,3,4];
let index = {o:4}
return arr[index.o];
};
for (var i = 0; i < 0x10000; ++i)
opt_me();
由于逃逸分析位于 Typer 之后(准确的说在 LoadElimination 之后,SimplifiedLowing 之前),因此 Typer 无法识别index.o 的值,只能当作 LoadField 节点访问1
2
3Type Typer::Visitor::TypeLoadField(Node* node) {
return FieldAccessOf(node->op()).type;
}
Type 结果为 Signed31,因此将 CheckBound 节点的 Type 优化为 Range(0,1073741822),成功绕过。并且不会影响到 SimplifiedLowing 对于 mode 的判断。
More
至此大概可以体会到,在新版的 V8 中利用 Typer bug 的难度增加了不少——关键在于将原本位置靠前的边界消除放置在了后面的 phase,所以需要保证在中间的 phase 的运行过程中,漏洞的利用条件不被破坏。因此从安全性的角度来看,这一 Patch 是很有效的。